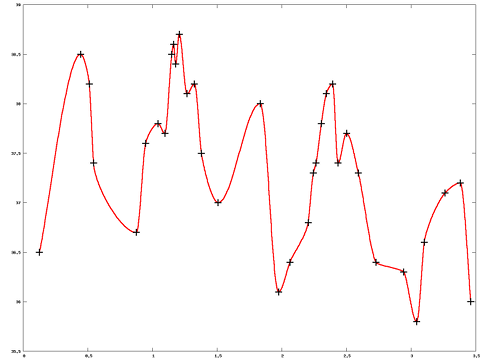
Das folgende Haskell-Programm berechnet Interpolationskurven, die folgenden Kriterien genügen:
-- Copyright (c) 2009 Jan Behrens
--
-- Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a
-- copy of this software and associated documentation files (the
-- "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including
-- without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish,
-- distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to
-- permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to
-- the following conditions:
--
-- The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included
-- in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
--
-- THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS
-- OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF
-- MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT.
-- IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY
-- CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT,
-- TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE
-- SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
enforceMonotony :: RealFloat a => [(a,a)] -> [(a,a)]
enforceMonotony (p1@(x1,_):p2@(x2,_):rest)
| x2 > x1 = p1 : enforceMonotony (p2:rest)
| otherwise = error "X values are not strictly monotonic increasing"
enforceMonotony points = points
guessSlopes :: RealFloat a => [(a,a)] -> [(a,a,a)]
guessSlopes points = beginWork (enforceMonotony points)
where
slope (x1,y1) (x2,y2) = (y2-y1) / (x2-x1)
beginWork all@(p1@(x1,y1):p2:_) = (x1, y1, slope p1 p2) : work all
beginWork _ = []
work [p1,p2@(x2,y2)] = [(x2, y2, slope p1 p2)]
work (p1@(x1,y1) : p2@(x2,y2) : p3@(x3,y3) : rest)
= (x2,y2,finalSlope) : work (p2:p3:rest)
where
leftSlope = slope p1 p2
rightSlope = slope p2 p3
mixAbsSlope = exp (((x3-x2) * log (abs leftSlope) +
(x2-x1) * log (abs rightSlope)) / (x3-x1))
finalSlope
| (y1 < y2) && (y2 < y3) = mixAbsSlope
| (y1 > y2) && (y2 > y3) = negate mixAbsSlope
| otherwise = 0
smoothPath :: RealFloat a => Int -> [(a,a)] -> [(a,a)]
smoothPath _ [] = []
smoothPath steps points = head points' : work (guessSlopes points')
where
points' = enforceMonotony points
work (d1:d2:rest) = pathPart d1 d2 ++ (work (d2:rest))
work _ = []
pathPart (x1,y1,s1) (x4,y4,s4)
| y1 == y4 = [(x4,y4)]
| otherwise = map interpolatePoint tx
where
rx = (x4-x1) / sqrt 2 / 2
ry = abs (y4-y1) / sqrt 2 / 2
dx2 = sqrt (1 / (1/rx^2 + s1^2/ry^2))
dy2 = s1 * dx2
x2 = x1 + dx2
y2 = y1 + dy2
dx3 = sqrt (1 / (1/rx^2 + s4^2/ry^2))
dy3 = s4 * dx3
x3 = x4 - dx3
y3 = y4 - dy3
tx = [ fromIntegral i / fromIntegral steps | i <- [1..steps]]
bezierX = bezier x1 x2 x3 x4
bezierY = bezier y1 y2 y3 y4
interpolatePoint t = (bezierX t, bezierY t)
bezier :: RealFloat a => a -> a -> a -> a -> a -> a
bezier x1 x2 x3 x4 t
= (1-t)^3 * x1 +
3 * t * (1-t)^2 * x2 +
3 * t^2 * (1-t) * x3 +
t^3 * x4
gnuplotScript :: RealFloat a => [(a,a)] -> String
gnuplotScript tuples
= "plot '-' notitle with lines\n" ++
concat (map tupleFormat tuples) ++ "e\n"
where
tupleFormat (x,y) = show x ++ " " ++ show y ++ "\n"
readPoints :: String -> [(Double, Double)]
readPoints input = work (lines input)
where
work [] = []
work (line:lines)
| parts == [] = work lines
| parts == ["e"] = []
| length parts == 2 = (read part1, read part2) : work lines
| otherwise = error "Parsing error"
where
parts = words line
[part1,part2] = parts
main = interact (gnuplotScript . smoothPath 60 . readPoints)
Die Datei smoothplot.hs ist herunterzuladen, und kann anschließend mit einem Haskell-Compiler compiliert werden:
$ ghc --make smoothplotEnthät die Datei "messwerte.txt" nun in jeder Zeile einen X-Wert gefolgt von Leerzeichen oder dem Tabulatorsteuerzeichen gefolgt von einem Y-Wert, dann lässt sich durch Eingabe des folgenden Kommandos eine Interpolationskurve zeichnen:
$ ./smoothplot < messwerte.txt | gnuplot -persist